Cloud Computing is a technology that enables access to computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, over the internet rather than maintaining these resources locally. In simple words its allows users to access and use computing services and resources on-demand through the internet.
With a variety of cloud architectures available, organizations can choose a model that best suits their needs in terms of scalability, security, and cost-effectiveness. we will explore the different types of cloud architecture
Public cloud is one of the most commonly used cloud architectures, provided by third-party vendors such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These services are available to the general public over the internet, allowing businesses to leverage computing resources without managing physical infrastructure.
Unlike public cloud, private cloud is dedicated to a single organization. This model provides enhanced security, control, and customization, making it suitable for industries handling sensitive data, such as finance, healthcare, and government.
What is hybrid cloud architecture?
Simply put, hybrid cloud architecture is a computing environment that integrates on-premises infrastructure, private cloud services, and public cloud platforms. It enables data and applications to move seamlessly between these environments, providing businesses with a balance between performance, cost efficiency, and control.
Why is Hybrid Cloud Gaining Traction?
Organizations are turning to hybrid cloud solutions for several key reasons:
- Flexibility and Scalability
- Businesses can scale up or down as needed, using public cloud resources during peak demand while keeping sensitive workloads in a private cloud.
- Cost Efficiency
- Instead of investing heavily in physical infrastructure, companies can leverage public cloud services for non-critical tasks, reducing overall costs.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance
- Sensitive data can be stored on private servers, while less critical applications run on public cloud platforms, helping organizations meet security and regulatory requirements.
Real-World Applications of Hybrid Cloud
Various industries are leveraging hybrid cloud strategies to streamline operations and improve service delivery:
- Healthcare: Hospitals use hybrid cloud models to securely store patient records while leveraging AI-powered public cloud tools for diagnostics.
- Finance: Banks keep customer data secure in private environments while using public cloud services for analytics and fraud detection.
- Retail: E-commerce platforms handle high traffic demands during sales events by scaling with public cloud resources while maintaining core databases in a private cloud.
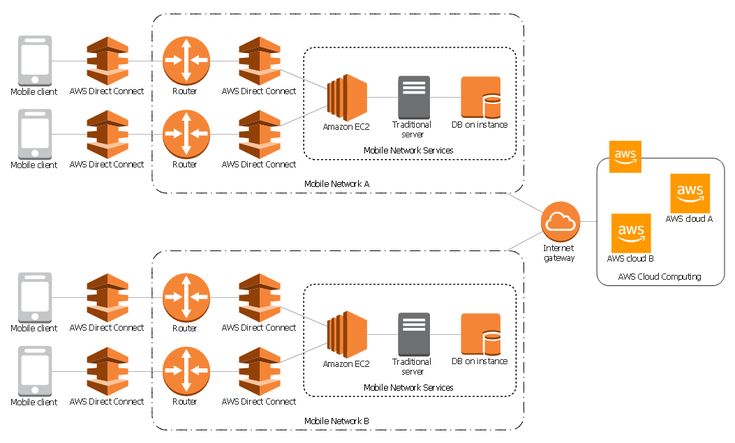
Hybrid Cloud Challenges
While hybrid cloud architecture offers numerous benefits, organizations must address certain challenges:
- Integration Complexity: Ensuring seamless connectivity between different cloud environments requires robust networking and security measures.
- Data Management: Businesses must implement efficient data governance policies to prevent duplication and security risks.
- Cost Optimization: Without proper planning, hybrid cloud costs can spiral due to unnecessary resource allocation.
How Choose the Right Cloud Architecture
Selecting the best cloud architecture depends on an organization’s requirements, including security, budget, and workload demands. While public cloud offers affordability and scalability, private and hybrid cloud solutions provide more control and security. Businesses looking for redundancy and flexibility may opt for multi-cloud, while community cloud is beneficial for shared industry-specific applications.


Awesome https://lc.cx/xjXBQT
Awesome
Good https://rb.gy/4gq2o4
Awesome
https://shorturl.fm/5JO3e
https://shorturl.fm/bODKa
Pingback: 100mg viagra