In today world cloud computing has emerged as more than just a buzzword—it’s become the backbone of modern digital operations. Whether you’re a startup looking to scale quickly or a well-established business aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs, cloud solutions and cloud services offer a path forward.
But with so many terms thrown around—public cloud, private cloud, hybrid models, SaaS, IaaS—it can be a bit overwhelming. I help with this blog break things down in a clear and relatable way to help you understand what cloud solutions and services are, how they work, and why they matter.
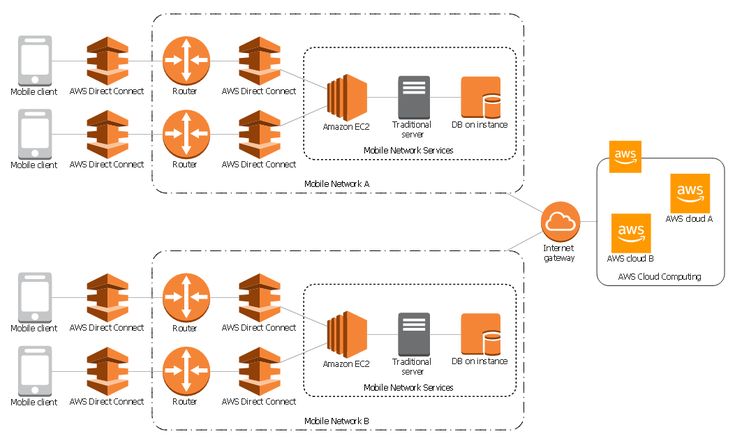
When we say cloud solutions, we’re referring to a broad range of computing services that are delivered over the internet. These can include everything from data storage and software hosting to powerful analytics platforms and artificial intelligence tools.
Think of it like this: instead of installing software on every individual computer or maintaining bulky servers in your office, you access what you need online—just like using Netflix instead of buying a DVD.
What Are Cloud Services?
Cloud services are the specific tools and platforms provided through the cloud. These services are usually categorized into three main types:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This is the most basic type of cloud service. With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure—servers, storage, and networking resources—from a provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure offer IaaS solutions.
Use Case: Ideal for businesses that want control over their IT resources without investing in physical hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a framework for developers to build and deploy applications without managing the underlying hardware or software layers.
Example: Google App Engine or Heroku.
Use Case: Great for software developers who want to focus on writing code without worrying about server maintenance.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, usually on a subscription basis. Users can access these apps through a web browser, making it easy to use them from anywhere.
Example: Gmail, Dropbox, Microsoft 365.
Use Case: Perfect for everyday users and businesses that need ready-to-use tools without installation hassles.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Not every cloud setup is the same. The deployment model you choose will depend on your company’s needs, budget, and existing infrastructure.
1. Public Cloud
This model uses shared infrastructure provided by third-party vendors. Resources are accessible to anyone who wants to purchase or subscribe.
Pros:
- Cost-effective
- Scalable
- No maintenance responsibilities
Cons:
- Less control over data
- Potential security concerns
2. Private Cloud
Built exclusively for a single organization, private clouds offer more control and security. These can be hosted on-site or by a third party.
Pros:
- Enhanced security
- Full control over infrastructure
Cons:
- More expensive
- Requires in-house IT expertise
3. Hybrid Cloud
As the name suggests, this is a blend of public and private clouds. Businesses can use the public cloud for general computing needs while keeping sensitive operations on a private server.
Pros:
- Flexibility
- Balanced cost and security
Cons:
- Complex to manage
- Requires robust integration
Why Businesses Are Embracing Cloud Services
There’s a reason why cloud adoption is growing rapidly—it offers clear and compelling benefits.
Cost Savings
With cloud services, businesses no longer need to invest heavily in physical infrastructure. You only pay for what you use, making it a budget-friendly option, especially for small businesses.
Scalability
Need more storage or computing power? Scale up with a few clicks. Cloud platforms are built to grow alongside your business needs.
Accessibility
Whether your team is in one office or spread across the globe, cloud services make it easy to collaborate and access files in real-time from any location.
Security
Contrary to popular belief, most reputable cloud providers offer advanced security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud solutions often include backup and disaster recovery features, ensuring your data is safe even if hardware fails or natural disasters strike.


Pingback: How Cloud Applications Work - Buzz Cloud Solution
Very good
Very good
Awesome
Good partner program https://shorturl.fm/N6nl1
Best partnership https://shorturl.fm/A5ni8
https://shorturl.fm/9fnIC
https://shorturl.fm/oYjg5
Pingback: sildenafil tab 25mg